Ansible基本概述
Ansible是一个配置管理系统configuration management system你只需要可以使用ssh访问你的服务器或设备就行。
Ansible能做什么
ansible可以帮助我们完成一些批量任务,或者完成一些需要经常重复的工作。
比如:同时在100台服务器上安装nginx服务,并在安装后启动服务。
比如:将某个文件一次性拷贝到100台服务器上。
比如:每当有新服务器加入工作环境时,你都要为新服务器部署某个服务,也就是说你需要经常重复的完成相同的工作。
这些场景中我们都可以使用到ansible。
Ansible软件特点
- ansible不需要单独安装客户端,SSH相当于ansible客户端。
- ansible不需要启动任何服务,仅需安装对应工具即可。
- ansible依赖大量的python模块来实现批量管理。
- ansible配置文件/etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
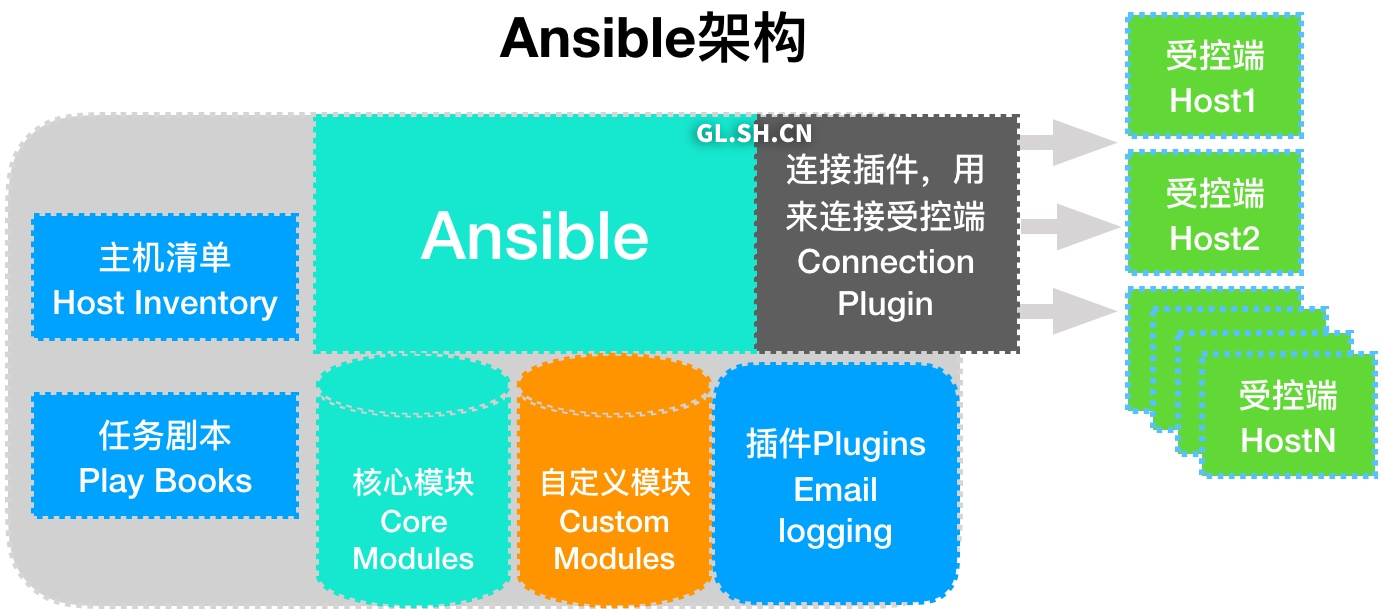
Ansible基础架构
- 连接插件(connectior plugins) 用于连接主机 用来连接被管理端
- 核心模块(core modules) 连接主机实现操作, 它依赖于具体的模块来做具体的事情
- 自定义模块(custom modules) 根据自己的需求编写具体的模块
- 插件(plugins) 完成模块功能的补充
- 剧本(playbooks)ansible的配置文件,将多个任务定义在剧本中,由ansible自动执行
- 主机清单(host inventory)定义ansible需要操作主机的范围
最重要的一点是 ansible是模块化的 它所有的操作都依赖于模块
Ansible安装配置
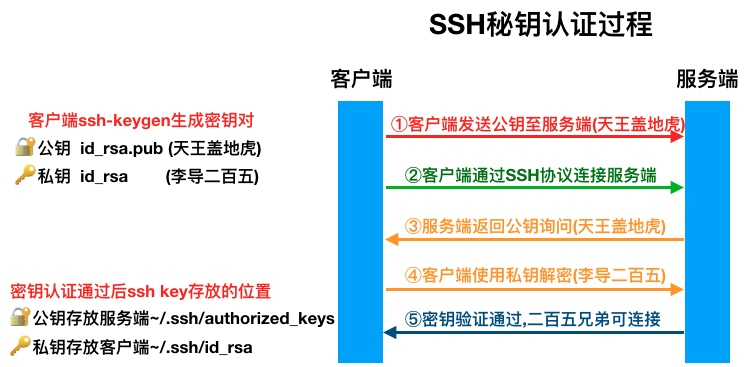
实现从管理机m01到其他机器的密钥认证
0.ansible借助公钥批量管理
#利用非交换式工具实现批量分发公钥与批量管理服务器
[root@m01 ~]# ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub root@172.16.1.41
[root@m01 ~]# ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub root@172.16.1.211.安装ansible
[root@m01 ~]# yum install ansible -y
//检查ansible版本
[root@m01 ~]# ansible --version
ansible 2.6.12.配置ansible
[root@m01 ~]# vim /etc/ansible/hosts
[guilin]
172.16.1.31
172.16.1.413.验证ansible
# ansible是通过ssh端口探测通信
[root@m01 ~]# ansible guilin -m ping
10.0.0.30 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
10.0.0.40 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}4 .ansible命令语法格式
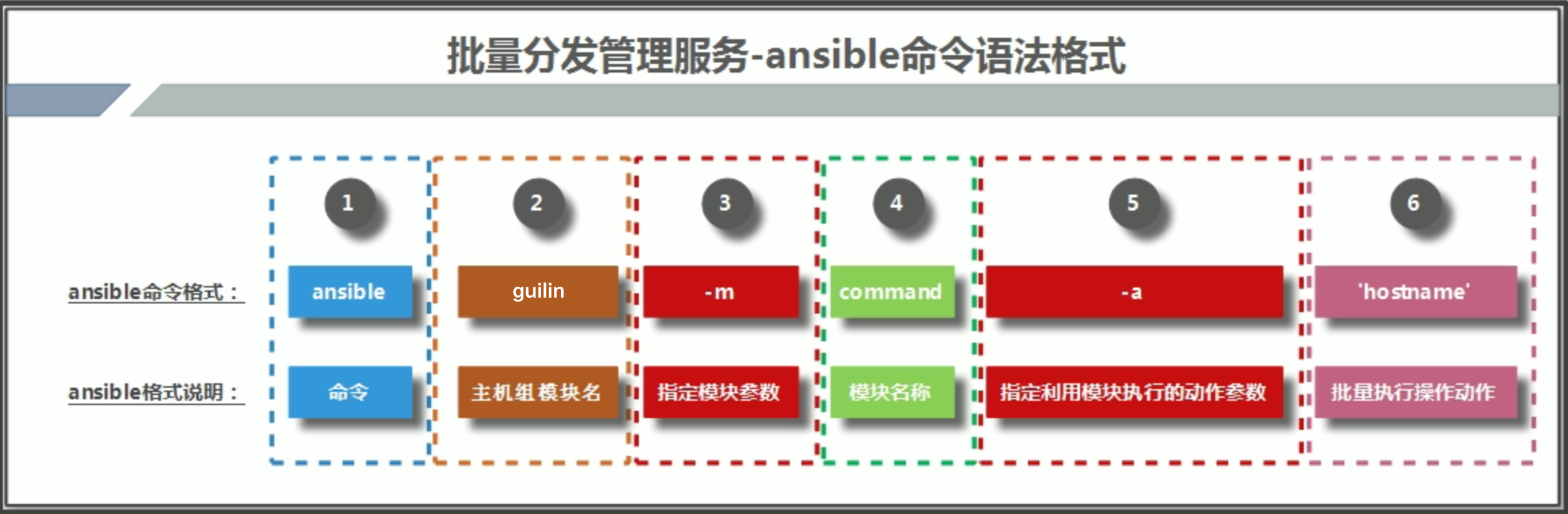
[root@m01 ~]# ansible guilin -m command -a "hostname"
10.0.0.31 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
backup
10.0.0.41 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
nfs01Ansible清单管理
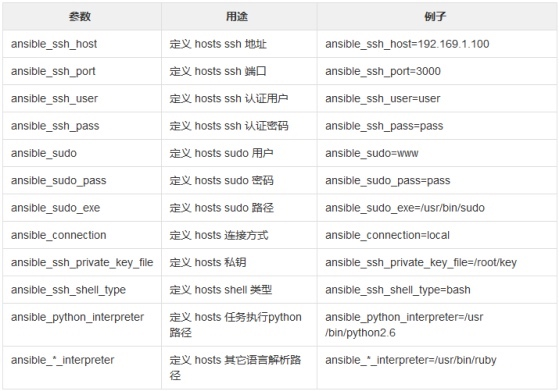
inventory文件通常用于定义要管理主机的认证信息, 例如ssh登录用户名、密码以及key相关信息。如何配置Inventory文件
主机
- 支持主机名通配以及正则表达式,例如web[1:3].gl.sh.cn
- 支持基于非标准的ssh端口,例如web1.gl.sh.cn:6666
- 支持指定变量,可对个别主机的特殊配置,如登陆用户,密码等
主机组
- 支持嵌套组,例如[game:children],那么在game模块下面的组都会被game所包含
- 支持指定变量,例如[game:vars]在下面指定变量
[root@gl.sh.cn ~]# cat /etc/ansible/hosts
[webservers]
10.0.0.8
10.0.0.31
10.0.0.41
10.0.0.61
# 添加三台主机至webserver[low版]
[webservers]
web1.gl.sh.cn
web2.gl.sh.cn
web3.gl.sh.cn
# 添加三台主机至webserver[low改良版]
[webservers]
web[1:3].gl.sh.cn
# 添加三台主机至webserver[密码版]
[webservers]
web1.gl.sh.cn ansible_ssh_pass='123456'
web2.gl.sh.cn ansible_ssh_pass='123456'
web3.gl.sh.cn ansible_ssh_pass='123456'
# 添加三台主机至webserver[密码改良版]
[webservers]
web[1:3].gl.sh.cn ansible_ssh_pass='123456'
# 添加三台主机至webserver[密码拆分版]
[webservers]
web1.gl.sh.cn
web2.gl.sh.cn
web3.gl.sh.cn
[webservers:vars]
ansible_ssh_pass='123456'
# 定义多组,多组汇总整合
[apache]
web1.gl.sh.cn
web2.gl.sh.cn
web3.gl.sh.cn
[apache:vars]
ansible_ssh_pass='123456'
[nginx]
10.0.0.7
10.0.0.31
10.0.0.41
10.0.0.61
[nginx:vars]
ansible_ssh_pass='123456'
# webservers组包括两个子组[apapche,nginx]
[webservers:children]
apache
nginx
ansible nginx --list-hosts
ansible apache --list-hosts
ansible websers --list-hostsAnsible内置变量
Ansible常用模块
在ansible中是指需要快速执行一条命令, 并且不需要保存的命令,对于复杂的命令则为playbook
Ansible注意事项->提示颜色信息说明
翔黄色:对远程节点进行相应修改
帽子绿:对远程节点不进行相应修改,或者只是对远程节点信息进行查看
深红色:操作执行命令有异常
浅紫色:表示对命令执行发出警告信息(可能存在的问题,给你一下建议)
1.command命令模块
# 默认模块, 执行命令
[root@m01 ~]# ansible guilin -a "hostname"
# 如果需要一些管道操作,则使用shell
[root@m01 ~]# ansible guilin -m shell -a "ifconfig|grep eth0" -f 50
# -f =forks /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg #结果返回的数量2.script脚本模块
# 编写脚本
[root@m01 ~]# mkdir -p /server/scripts
[root@m01 ~]# cat /server/scripts/yum.sh
#!/usr/bin/bash
yum install -y iftop
#在本地运行模块,等同于在远程执行,不需要将脚本文件进行推送目标主机执行
[root@m01 ~]# ansible guilin -m script -a "/server/scripts/yum.sh"3.yum安装软件模块
[root@m01 ~]# ansible guilin -m yum -a "name=httpd state=installed"
name ---指定要安装的软件包名称
state ---指定使用yum的方法
installed,present ---安装软件包
removed,absent ---移除软件包
latest ---安装最新软件包4.copy文件拷贝模块
# 推送文件模块
[root@m01 ~]# ansible guilin -m copy -a "src=/etc/hosts dest=/tmp/test.txt"
# 在推送覆盖远程端文件前,对远端已有文件进行备份,按照时间信息备份
[root@m01 ~]# ansible guilin -m copy -a "src=/etc/hosts dest=/tmp/test.txt backup=yes"
# 直接向远端文件内写入数据信息,并且会覆盖远端文件内原有数据信息
[root@m01 ~]# ansible guilin -m copy -a "content='bgx' dest=/tmp/guilin"
src --- 推送数据的源文件信息
dest --- 推送数据的目标路径
backup --- 对推送传输过去的文件,进行备份
content --- 直接批量在被管理端文件中添加内容
group --- 将本地文件推送到远端,指定文件属组信息
owner --- 将本地文件推送到远端,指定文件属主信息
mode --- 将本地文件推送到远端,指定文件权限信息5.file文件配置模块
[root@m01 ~]# ansible guilin -m file -a "path=/tmp/guilin state=diretory"
[root@m01 ~]# ansible guilin -m file -a "path=/tmp/tt state=touch mode=555 owner=root group=root"
[root@m01 ~]# ansible guilin -m file -a "src=/tmp/tt path=/tmp/tt_link state=link"
path --- 指定远程主机目录或文件信息
recurse --- 递归授权
state ---
directory --- 在远端创建目录
touch --- 在远端创建文件
link --- link或hard表示创建链接文件
absent --- 表示删除文件或目录
mode --- 设置文件或目录权限
owner --- 设置文件或目录属主信息
group --- 设置文件或目录属组信息6.service服务模块
[root@m01 ~]# ansible guilin -m service -a "name=crond state=stopped enabled=yes"
name # 定义要启动服务的名称
state # 指定服务状态是停止或是运行,停止和运行指令要写成过去时
started # 启动
stopped # 停止
restarted # 重启
reloaded # 重载
enabled # 是否让服务开启自启动7.group组模块
[root@m01 ~]# ansible guilin -m group -a "name=bb gid=888"
name # 指定创建的组名
gid # 指定组的gid
state
absent # 移除远端主机的组
present # 创建远端主机的组(默认)8.user模块
# -1使用MD5进行加密 -stdin 非交互式 -salt 加密参数
[root@m01 ~]# echo "cgl"| openssl passwd -1 -stdin -salt 'salt'
[root@m01 ~]# ansible guilin -m user -a "name=bb uid=888 group=888 shell=/sbin/nologin create_home=no"
[root@m01 ~]# ansible guilin -m user -a "name=ndy password='$1$765yDGau$diDKPRPMU6KEVEaPTZ0'"
uid # 指定用户的uid
group # 指定用户组名称
groups # 指定附加组名称
password # 给用户添加密码
shell # 指定用户登录shell
create_home # 是否创建家目录8.crond定时任务模块
# 正常使用crond服务
[root@m01 ~]# crontab -l
* * * * * /bin/sh /server/scripts/yum.sh
# 使用ansible添加一条定时任务
[root@m01 ~]# ansible guilin -m cron -a "minute=* hour=* day=* month=* weekday=* job='/bin/sh /server/scripts/test.sh'"
[root@m01 ~]# ansible guilin -m cron -a "job='/bin/sh /server/scripts/test.sh'"
# 设置定时任务注释信息,防止重复,name设定
[root@m01 ~]# ansible guilin -m cron -a "name='cron01' job='/bin/sh /server/scripts/test.sh'"
# 删除相应定时任务
[root@m01 ~]# ansible guilin -m cron -a "name='ansible cron02' minute=0 hour=0 job='/bin/sh /server/scripts/test.sh' state=absent"
# 注释相应定时任务,使定时任务失效
[root@m01 scripts]# ansible guilin -m cron -a "name='ansible cron01' minute=0 hour=0 job='/bin/sh /server/scripts/test.sh' disabled=no"9.mount模块
[root@m01 ~]# ansible guilin -m mount -a "src=172.16.1.31:/data path=/data fstype=nfs opts=defaults state=present"
[root@m01 ~]# ansible web -m mount -a "src=172.16.1.31:/data path=/data fstype=nfs opts=defaults state=mounted"
[root@m01 ~]# ansible web -m mount -a "src=172.16.1.31:/data path=/data fstype=nfs opts=defaults state=unmounted"
[root@m01 ~]# ansible web -m mount -a "src=172.16.1.31:/data path=/data fstype=nfs opts=defaults state=absent"
present # 开机挂载,仅将挂载配置写入/etc/fstab
mounted # 挂载设备,并将配置写入/etc/fstab
unmounted # 卸载设备,不会清除/etc/fstab写入的配置
absent # 卸载设备,会清理/etc/fstab写入的配置10.ansible查看帮助方法
[root@m01 ~]# ansible-doc -l --- 查看所有模块说明信息
[root@m01 ~]# ansible-doc copy --- 表示指定查看某个模块参数用法信息Ansible Playbook
playbook是由一个或多个模块组成的,使用多个不同的模块,完成一件事情。
playbook通过yaml语法识别描述的状态文件。扩展名是yaml
1.YAML三板斧
- 缩进
- YAML使用一个固定的缩进风格表示层级结构,每个缩进由两个空格组成, 不能使用tabs
- 冒号
- 以冒号结尾的除外,其他所有冒号后面所有必须有空格。
- 短横线
- 表示列表项,使用一个短横杠加一个空格。
- 多个项使用同样的缩进级别作为同一列表。
2.ansible playbook安装Apache示例
您暂时无权查看此隐藏内容!Ansible项目案例
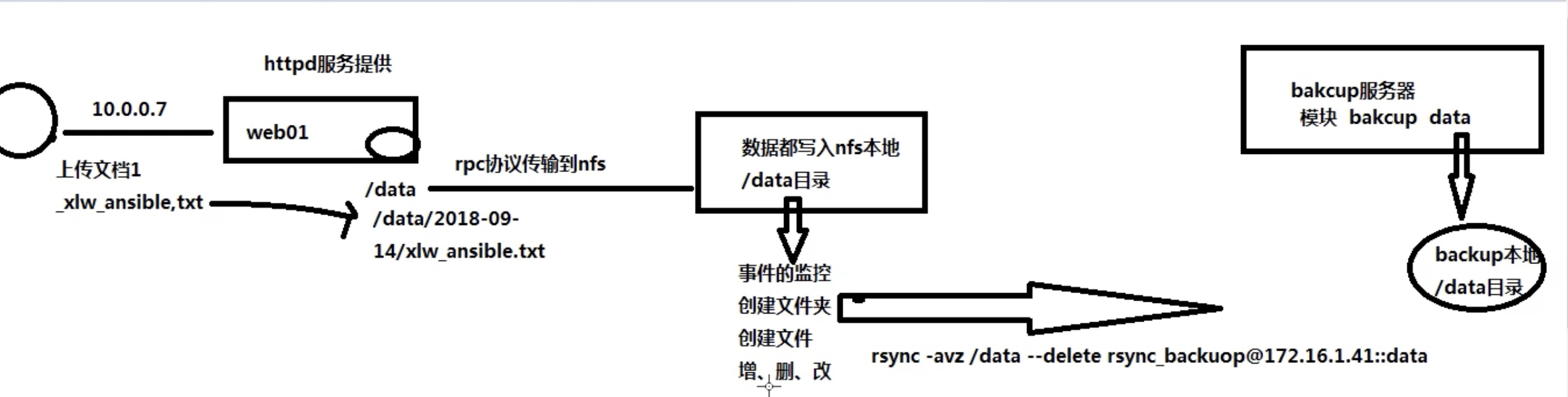
1.环境规划
| 角色 | 外网IP(NAT) | 内网IP(LAN) | 部署软件 |
|---|---|---|---|
| m01 | eth0:10.0.0.61 | eth1:172.16.1.61 | ansible |
| backup | eth0:10.0.0.41 | eth1:172.16.1.41 | rsync |
| nfs | eth0:10.0.0.31 | eth1:172.16.1.31 | nfs、Sersync |
| web01 | eth0:10.0.0.7 | eth1:172.16.1.7 | httpd |
2.配置ansible对应的主机
[root@m01 ~]# vim /etc/ansible/hosts
[web]
172.16.1.7
[nfs]
172.16.1.31
[backup]
172.16.1.413.检查对应的主机组和规划的IP是否一致
[root@m01 ~]# ansible web --list-host
hosts (1):
172.16.1.7
[root@m01 ~]# ansible backup --list-host
hosts (1):
172.16.1.41
[root@m01 ~]# ansible nfs --list-host
hosts (1):
172.16.1.31
[root@m01 ~]# ansible all --list-host
hosts (3):
172.16.1.31
172.16.1.41
172.16.1.74.建立对应的目录站点,用于存放ansible-playbook文件
[root@m01 ~]# mkdir -p /etc/ansible/ansible_playbook/{conf,file} -p
[root@m01 ~]# cd /etc/ansible/ansible_playbook/
[root@m01 ansible_playbook]# ll
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 6 Aug 1 10:30 conf
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 6 Aug 1 10:30 file5.编写基础模块的palybook
0.基础仓库准备
1.安装rsync
2.安装nfs-utils
3.创建www用户指定uid、gid
4.准备rsync客户端密码文件
1.建立基础环境的yaml
您暂时无权查看此隐藏内容!2.使用ansible-playbook检测语法, 并进行模拟执行
# 检测语法
[root@m01 ansible_playbook]# ansible-playbook --syntax-check base.yaml
playbook: base.yaml
# 模拟执行
[root@m01 ansible_playbook]# ansible-playbook -C base.yaml6.编写应用模块rsync的palybook
1.安装rsync
2.配置rsync
3.启动rsync
4.准备对应数据存储仓库/backup /data 授权为www
5.准备虚拟用户和密码文件,权限600
6.变更配置,重载服务
1.准备对应的配置文件存放至/etc/ansible/ansible_playbook/conf/
[root@m01 conf]# cat /etc/ansible/ansible_playbook/conf/rsyncd.conf
uid = www
gid = www
port = 873
fake super = yes
use chroot = no
max connections = 200
timeout = 600
ignore errors
read only = false
list = false
auth users = rsync_backup
secrets file = /etc/rsync.passwd
log file = /var/log/rsyncd.log
#####################################
[backup]
path = /backup
[data]
path = /data2.编写rsync安装的的yaml语法
您暂时无权查看此隐藏内容!7.编写应用模块nfs的palybook
1.安装nfs
2.配置nfs
3.启动nfs
4.准备对应数据存储仓库/data授权为www
5.变更配置,重载服务
1.准备nfs配置文件exports
[root@m01 ansible_playbook]# cat /etc/ansible/ansible_playbook/conf/nfs_exports
/data/ 172.16.1.0/24(rw,sync,all_squash,anonuid=666,anongid=666)2.编写nfs安装与配置的yaml
您暂时无权查看此隐藏内容!8.编写应用模块sersync的palybook
1.安装sersync
2.配置sersync
3.启动sersync
1.下载Sersync软件包
[root@m01 ansible_playbook]# ll /etc/ansible/ansible_playbook/file/
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 727290 Aug 1 12:04 sersync.tar.gz2.准备sersync实时同步的配置文件
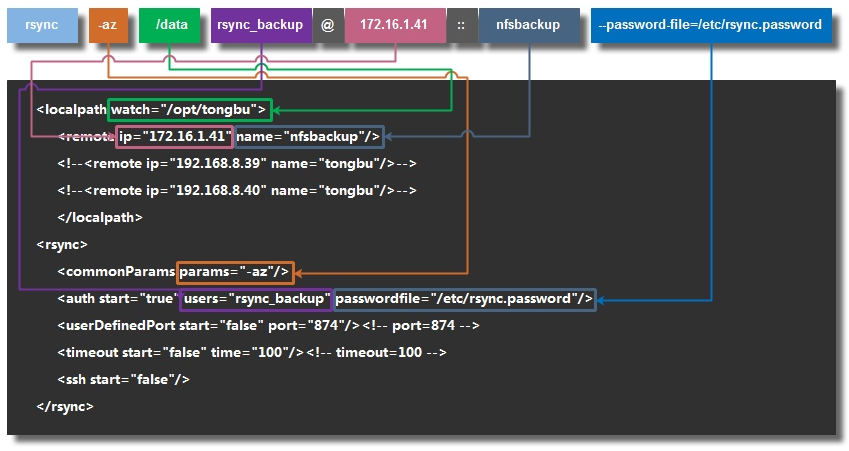
[root@m01 ansible_playbook]# cat /etc/ansible/ansible_playbook/conf/confxml.xml.nfs
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?>
<head version="2.5">
<host hostip="localhost" port="8008"></host>
<debug start="false"/>
<fileSystem xfs="true"/>
<filter start="false">
<exclude expression="(.*)\.svn"></exclude>
<exclude expression="(.*)\.gz"></exclude>
<exclude expression="^info/*"></exclude>
<exclude expression="^static/*"></exclude>
</filter>
<inotify>
<delete start="true"/>
<createFolder start="true"/>
<createFile start="true"/>
<closeWrite start="true"/>
<moveFrom start="true"/>
<moveTo start="true"/>
<attrib start="false"/>
<modify start="false"/>
</inotify>
<sersync>
<localpath watch="/data">
<remote ip="172.16.1.41" name="data"/>
</localpath>
<rsync>
<commonParams params="-az"/>
<auth start="true" users="rsync_backup" passwordfile="/etc/rsync.pass"/>
<userDefinedPort start="false" port="874"/><!-- port=874 -->
<timeout start="true" time="100"/><!-- timeout=100 -->
<ssh start="false"/>
</rsync>
<failLog path="/tmp/rsync_fail_log.sh" timeToExecute="60"/><!--default every 60mins execute once-->
<crontab start="false" schedule="600"><!--600mins-->
<crontabfilter start="false">
<exclude expression="*.php"></exclude>
<exclude expression="info/*"></exclude>
</crontabfilter>
</crontab>
<plugin start="false" name="command"/>
</sersync>
<plugin name="command">
<param prefix="/bin/sh" suffix="" ignoreError="true"/> <!--prefix /opt/tongbu/mmm.sh suffix-->
<filter start="false">
<include expression="(.*)\.php"/>
<include expression="(.*)\.sh"/>
</filter>
</plugin>
<plugin name="socket">
<localpath watch="/opt/tongbu">
<deshost ip="192.168.138.20" port="8009"/>
</localpath>
</plugin>
<plugin name="refreshCDN">
<localpath watch="/data0/htdocs/cms.xoyo.com/site/">
<cdninfo domainname="ccms.chinacache.com" port="80" username="xxxx" passwd="xxxx"/>
<sendurl base="http://pic.xoyo.com/cms"/>
<regexurl regex="false" match="cms.xoyo.com/site([/a-zA-Z0-9]*).xoyo.com/images"/>
</localpath>
</plugin>
</head>3.编写sersync应用的yaml
您暂时无权查看此隐藏内容!9.编写web应用模块的palybook
[root@m01 ansible_playbook]# cat web.yaml
- hosts: web
tasks:
- name: Create Nfs Client Data
file: path=/data state=directory
- name: Mount Nfs Server
mount: path=/data src=nfs01:/data fstype=nfs opts=defaults state=mounted10.将所有编写好的yaml引入至一个文件中, 这样便于一次执行
[root@m01 ansible_playbook]# cat main.yaml
- import_playbook: base.yaml
- import_playbook: rsync.yaml
- import_playbook: nfs.yaml
- import_playbook: sersync.yaml
- import_playbook: web.yaml11.测试
1.先测试web是否能同步数据至nfs存储
2.nfs是否实时同步至rsync的/data
3.使用客户端测试能否推送数据至rsync的backup

 Asynq任务框架
Asynq任务框架 MCP智能体开发实战
MCP智能体开发实战 WEB架构
WEB架构 安全监控体系
安全监控体系